In this React 16+ tutorial, we’ll learn how to add drag and drop functionality on components in ReactJs application and create a simple working example with the help of react-draggable package module.
In modern applications, a user expects a lot of interaction making interfaces more friendly and easy to go with. One such feature is to enable draggable elements on the page where users can play by dragging sections according to their priorities.
Today we will create an example of ReactJs application and discuss the important properties and event handlers available to track the movement.
Let’s get in…
Create a React Application
First, we’ll create a new React application using npx create-react-app command
$ npx create-react-app react-select-appMove inside the react app
$ cd react-select-appRun application
$ npm start
Install React Draggable Package
Next, we’ll install the react-draggable package in the application by running below command in the terminal
$ npm install react-draggable
Adding Draggable Component
Adding a drag feature to a component is very easy. Import the Draggable class from 'react-draggable', then wrap the elements with <Draggable> component to make them draggable on the page.
// App.js
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Draggable from 'react-draggable';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Draggable>
<div className="drag-box">
<div>I am ready to be Dragged!!!</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
);
}
}
export default App;
Also, add the following CSS in the App.css file
.drag-box {
padding: 30px;
background: #ccc;
width: 100px;
cursor: move;
}Now run the Reactjs app by hitting $ npm start command.
Callback Methods and Event Handling
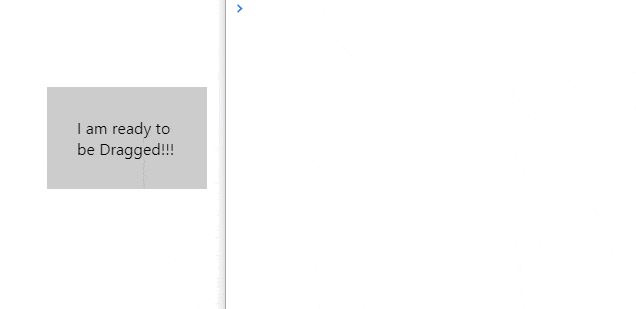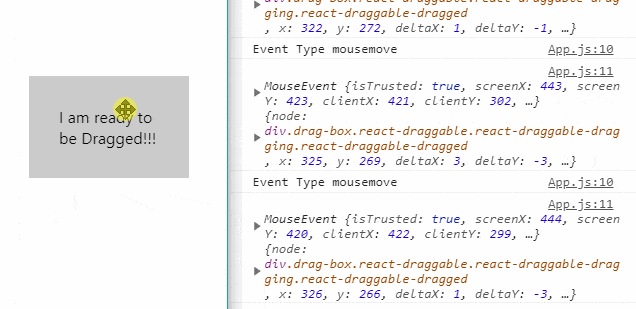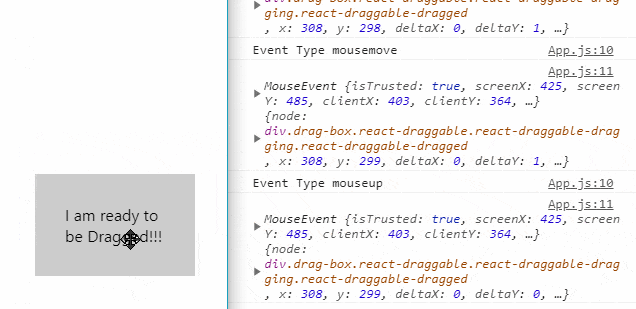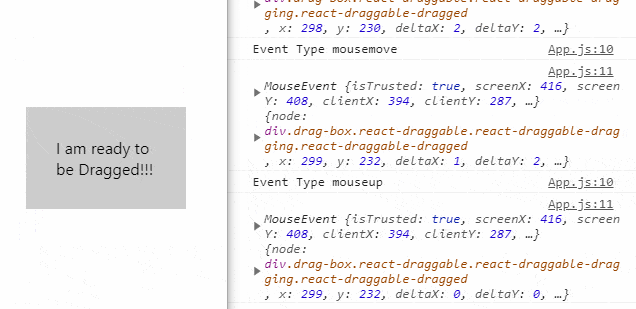
The Draggable component supports the following callback methods to track events of the Drag movement of the elements:
onDrag(): Triggered when drag is in process.onStart(): Triggered when dragging starts.onStop(): Triggered when dragging stops.onMouseDown(): Triggered when mouse is pressed to start drag.onMouseUp(): Triggered when the mouse is left before stoping the drag.onTouchStart(): Triggered in touch environment before drag start.onTouchEnd(): Triggered in touch environment before drag stops.
Using Event Callbacks on Draggable
Event handlers can be added on the Draggable component and defined inside the render() method
class App extends React.Component {
handleEvent = (e, data) => {
console.log('Event Type', e.type);
console.log(e, data);
}
render() {
return (
<Draggable
onDrag={this.handleEvent}
onStart={this.handleEvent}
onStop={this.handleEvent}
onMouseDown={this.handleEvent}
onMouseUp={this.handleEvent}
onTouchStart={this.handleEvent}
onTouchEnd={this.handleEvent}>
<div className="drag-box">
<div>I am ready to be Dragged!!!</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
);
}
}
Drag in a specific axis or direction
The axis property is used to force dragging in a specific direction. It takes these values ‘both‘, ‘x‘, ‘y‘ & ‘none‘ where ‘both’ is the default.
This will drag on the x-axis only.
<Draggable
axis="x"
>
<div className="drag-box">
<div>Dragging horizontally</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
Define a Handle to Drag
Instead of dragging the element by picking from anywhere, we can set a selector in the Draggable component which can be picker to drag.
To enable we add the handle property
<Draggable
handle="#imhandle"
>
<div className="drag-box">
<span id="imhandle">I am Handle</span>
<div>Handle with Care</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
Track Position of Draggable
The delta position of the X and Y axis can be tracked as follows:
// App.js
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Draggable from 'react-draggable';
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
activeDrags: 0,
deltaPosition: {
x: 0, y: 0
}
};
handleDrag = (e, ui) => {
const { x, y } = this.state.deltaPosition;
this.setState({
deltaPosition: {
x: x + ui.deltaX,
y: y + ui.deltaY,
}
});
};
render() {
const { deltaPosition } = this.state;
return (
<Draggable
onDrag={this.handleDrag}>
<div className="drag-box">
<div>Tacking Delta</div>
<div>x: {deltaPosition.x.toFixed(0)}, y: {deltaPosition.y.toFixed(0)}</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
);
}
}
export default App;Here we defined state to keep values then initialized then in the render() method. The onDrag() event handler is tracking and updating the state using setState inside the handler method with Delta position.
Defining Limitation and Boundaries for Draggable Elements
The bounds property can be used to define and limit the draggable area for the element
Defined Bounds
The bounds property can be used to well define the area in px from the current position.
<Draggable
bounds={{ top: -100, left: -100, right: 100, bottom: 100 }}>
<div className="drag-box">
<div>I can only be moved 100px in any direction.</div>
</div>
</Draggable>
Parent as bound
The element can be dragged inside the parent by defining bounds="parent"
return (
<div className="box" style={{ height: '500px', width: '500px', position: 'relative', overflow: 'auto', padding: '0' }}>
<div style={{ height: '1000px', width: '1000px', padding: '10px' }}>
<Draggable bounds="parent">
<div className="drag-box">
I can only be moved within my offsetParent.<br /><br />
Both parent padding and child margin work properly.
</div>
</Draggable>
</div>
</div>
);
Drag inside the page body
By setting bounds="body" the element will drag inside the visible page
<Draggable bounds="body">
<div className="drag-box">
I can only be moved within the confines of the body element.
</div>
</Draggable>
Grid Movement Drag
In the blocked or Grid-based UI we can set the grid property to drag in snaps of defined height and width
<Draggable grid={[100, 100]} >
<div className="drag-box">I snap to a 100 x 100 grid</div>
</Draggable>
Conclusion
We have discussed how to introduce the draggable feature in the ReacJs application by installing the react-draggable package. We discussed many important features and properties that can be used to build real-world applications.
You can check more details on the official documentation.
Feel free to share your thoughts links on which you have used this functionality…